Why A Vibrating Screen

Since the dawn of time, and in every civilization, there has been a need to classify materials, and efforts have been made throughout history to find simpler, faster and more efficient ways of classifying materials.
As a result of these efforts, many different types of mechanisms have been developed and improved aimed at finding the optimum approach in material operations, and these solutions named as .

Materials thanks to effect of mechanical vibration. The body of the is vibrated by a vibration mechanism, causing the whole to shake. The material that needs to be sorted is classified on an equal basis under the effect of vibrating forces while passing over a sieve media. At the end of this process, the material is classified into the desired dimensions.
Nowadays, mechanical are able to serve in a wide range of application areas due to their simple and effective classification approach. For example, companies engaged in stone quarrying, mining fields, ore processing and recycling operations are the primary sectors employing vibrating .

Types are categorized in terms of:
- Vibrating mechanism
- Operating frequency
- Sieving media
- Installation angle
- Vibrating motion
- Wet or dry abilities
Each of these types have their own advantages and disadvantages, but if used in an appropriate manner, all of the disadvantages may be eliminated easily, as each has been designed for a specific purpose. As a result of this approach, many problems have been solved and the optimum solution has been obtained in operations.
Vibrating Definitions and Terminology
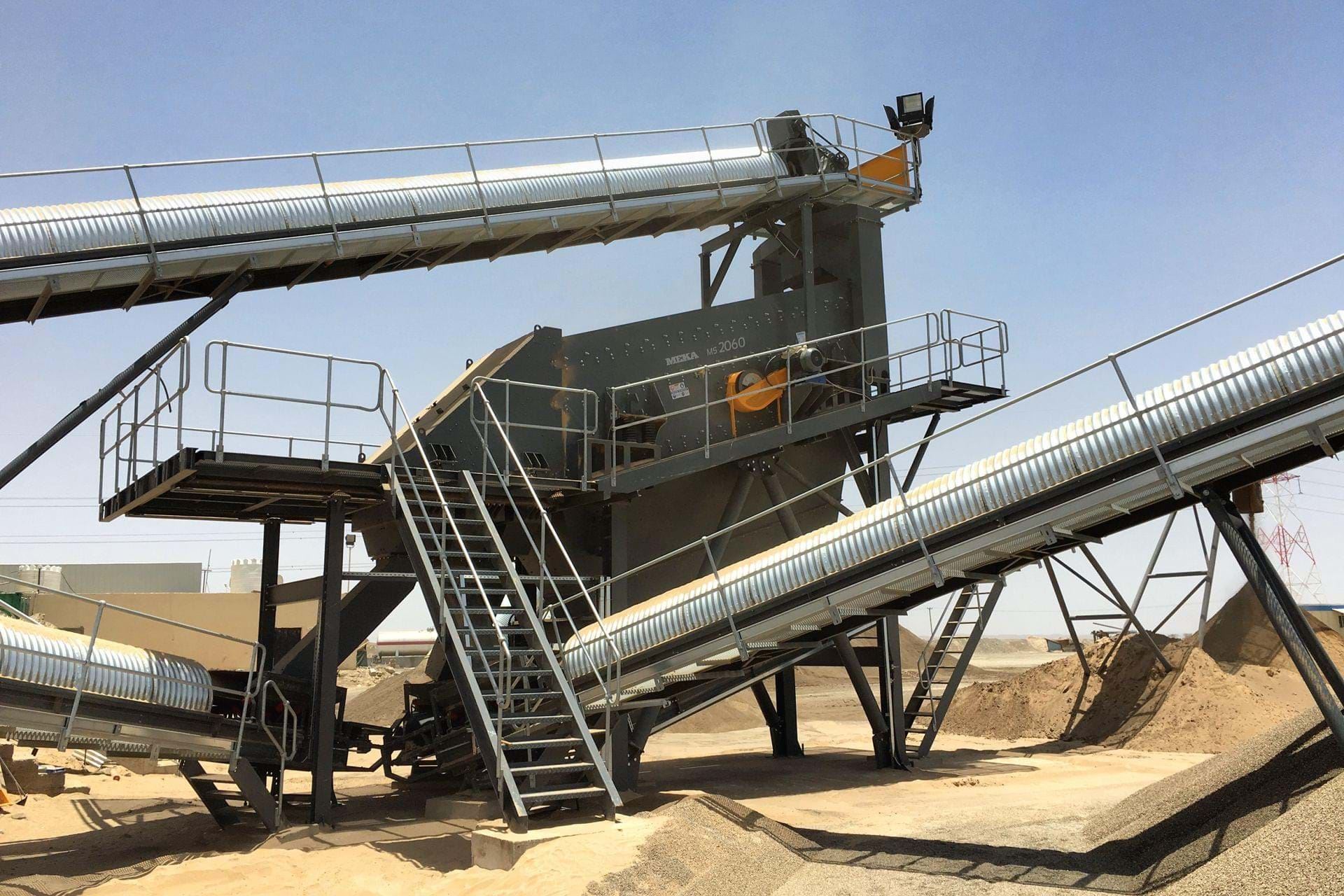

To gain a good understanding of the body of literature on , it is first necessary to familiarize oneself with the terminology in the field. This manual clarifies the terms relating to both the procedure and the themselves.
Amplitude:A measurement of cloth as it vertically peaks to its tallest height and troughs to it lowest point. Measured in multiples of the acceleration constant “g” [g-force]
Stroke: Double the amount of amplitude
Blinding: Event of material plugging in to the open slots of media.
Media: Sieving material defined by mesh size. It can be made from stainless steel, polyurethane, rubber or punched steel plate.
Deck: A frame that holds the media in place. could have multiple deck.
Frequency: Measured in Hertz [Hz] or revolutions per minute [RPM] and is the number of times that the media peaks and troughs with in under the seconds.
Gradation: Material grading. Given a feed material in an initial state. The material can be defined to have a particle size distribution. Grading is defining the maximum and minimum material sizes by way of mesh selection.
Stratification: The phenomenon occurs as vibration is passed through the bed of material causing larger material to rise and the finer material to descend within the bed.
Scalping:Refers to removal of the larger size particles from incoming material.
Exciter: Refers to the vibration source.
G-Force: Refers to the force of acceleration on the .